A Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM) is a critical document for ensuring project alignment and quality assurance. It maps requirements to corresponding project artifacts, such as test cases, test results, and identified issues, ensuring a seamless link between project objectives and outcomes.
By using an RTM:
- Requirements are effectively tracked from inception to completion.
- Testing efforts become more focused, as testers can quickly identify which requirements each test case validates.
- Project risks are minimized, as any gaps in coverage or deviations from requirements are immediately noticeable.
The RTM is not just a tool for tracking but also for maintaining transparency and accountability, ultimately contributing to a higher-quality application and more efficient project workflows.
Key Benefits of a Requirements Traceability Matrix (RTM)
-
Alignment
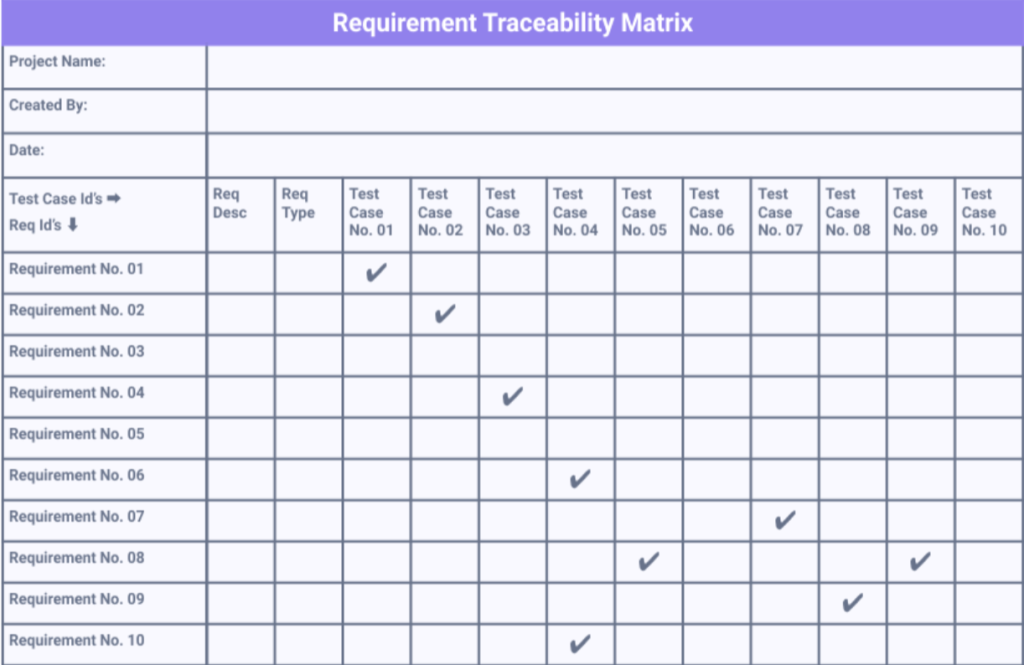
- RTM ensures every requirement outlined by stakeholders is mapped to one or more test cases.
- This comprehensive mapping validates that all requirements are adequately tested, reducing the risk of missing critical functionalities.
-
Traceability
- RTM provides a bidirectional link between requirements and test cases, allowing teams to trace backward (test case to requirement) or forward (requirement to test case).
- This facilitates clear communication among team members, streamlining collaboration and issue resolution.
-
Impact Analysis
- By identifying the requirements affected by system or application changes, RTM helps assess the impact of those changes.
- This capability aids in prioritizing testing efforts and ensuring changes do not introduce unforeseen issues.
-
Documentation
- RTM acts as a centralized repository that captures the relationships between requirements and test cases.
- It enhances transparency, supports accountability, and provides a valuable reference for audits or future projects.
By leveraging an RTM, teams can maintain project alignment, improve testing efficiency, and ensure high-quality deliverables.
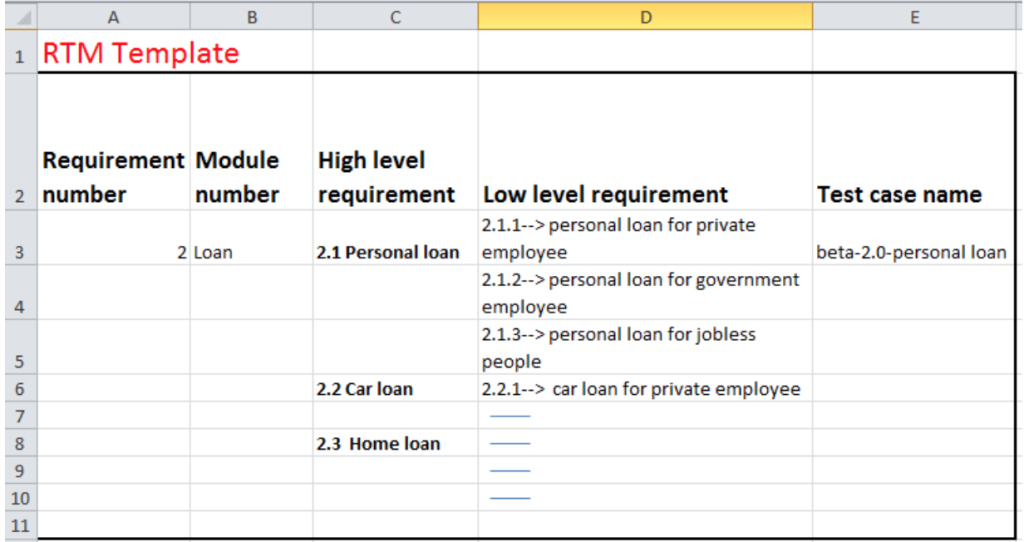
Types of Traceability Matrix:- There are 3 types of traceability matrix:
- Forward traceability matrix
- Backward traceability matrix
- Bi-directional traceability matrix

Bottomline :
To ensure a smooth transition to RTM, it’s essential to understand its extended benefits:
-
- Identify Extra Test Cases: RTM helps pinpoint additional test cases that were added beyond the specified requirements. This insight ensures clarity about whether these extra test cases address potential risks, enhance coverage, or are redundant.
-
- Track Test Status: RTM makes it easier to monitor the overall test status by providing a clear overview of which requirements have been tested, which are pending, and any associated test outcomes.
These features enhance project visibility and ensure that testing efforts align effectively with project goals, making RTM an indispensable tool for quality assurance.







